Publication: Deletion of the mRNA endonuclease Regnase-1 promotes NK cell anti-tumor activity via OCT2-dependent transcription of Ifng
Published in: Immunity, 2024, 57 (6), pp.1360-1377.e13. ⟨10.1016/j.immuni.2024.05.006⟩
Authors: Xin Sun, Yasuharu Nagahama, Shailendra Kumar Singh, Yuuki Kozakai, Hiroshi Nabeshima, Kiyoharu Fukushima, Hiroki Tanaka, Daisuke Motooka, Eriko Fukui, Eric Vivier, Diego Diez, Shizuo Akira
Summary
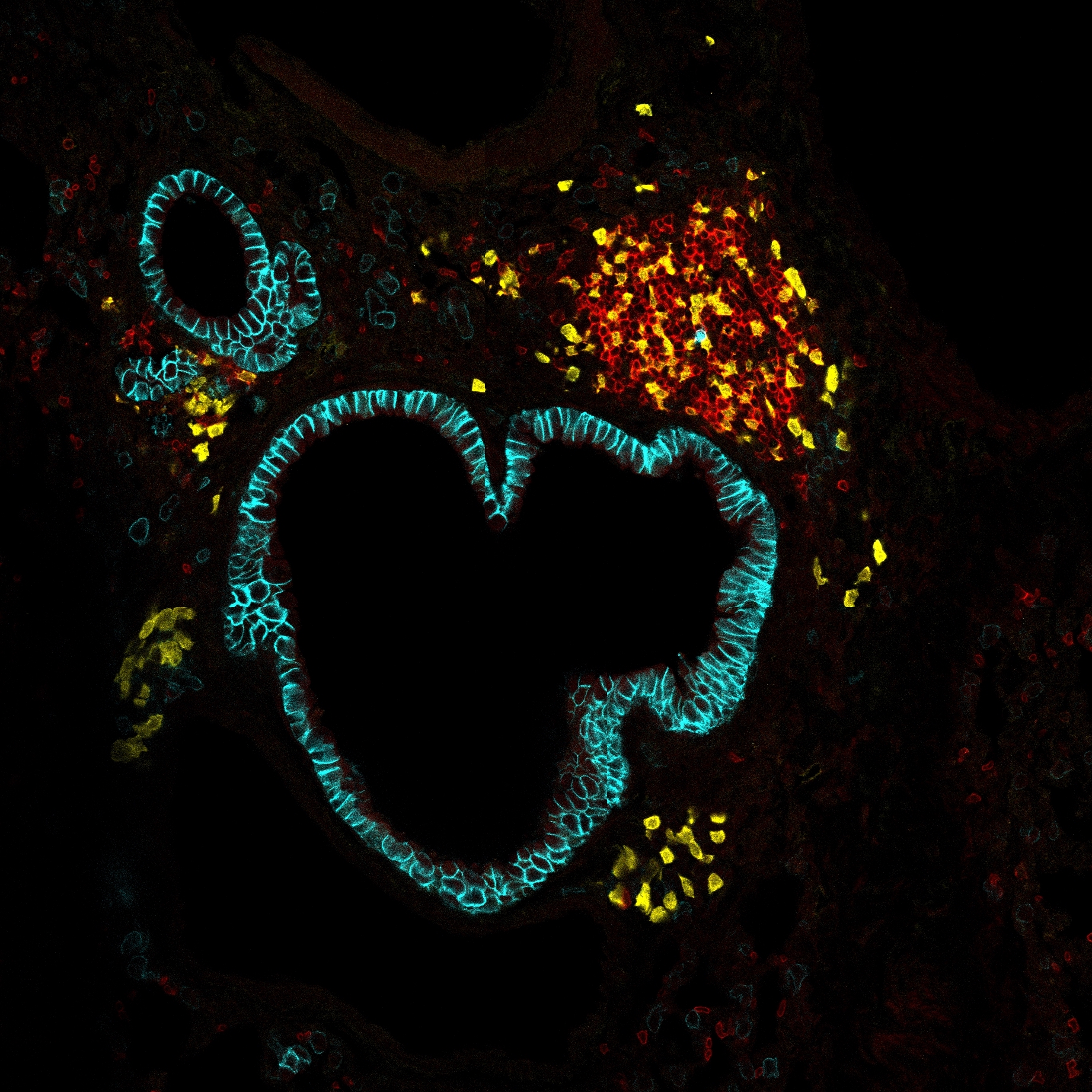
Limited infiltration and activity of natural killer (NK) and T cells within the tumor microenvironment (TME) correlate with poor immunotherapy responses. Here, we examined the role of the endonuclease Regnase-1 on NK cell anti-tumor activity. NK cell-specific deletion of Regnase-1 (Reg1ΔNK) augmented cytolytic activity and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) production in vitro and increased intra-tumoral accumulation of Reg1ΔNK-NK cells in vivo, reducing tumor growth dependent on IFN-γ. Transcriptional changes in Reg1ΔNK-NK cells included elevated IFN-γ expression, cytolytic effectors, and the chemokine receptor CXCR6. IFN-γ induced expression of the CXCR6 ligand CXCL16 on myeloid cells, promoting further recruitment of Reg1ΔNK-NK cells. Mechanistically, Regnase-1 deletion increased its targets, the transcriptional regulators OCT2 and IκBζ, following interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-18 stimulation, and the resulting OCT2-IκBζ-NF-κB complex induced Ifng transcription. Silencing Regnase-1 in human NK cells increased the expression of IFNG and POU2F2. Our findings highlight NK cell dysfunction in the TME and propose that targeting Regnase-1 could augment active NK cell persistence for cancer immunotherapy.
Link to HAL – amu-04934570
Link to DOI – 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.05.006