Publication: Tissue-resident macrophages in omentum promote metastatic spread of ovarian cancer
Published in: J Exp Med 2020 Apr; 217(4):
Authors: Anders Etzerodt, Morgane Moulin, Thomas Koed Doktor, Marcello Delfini, Noushine Mossadegh, Marc Bajenoff, Michael H. Sieweke, Søren Kragh Moestrup, Nathalie Auphan-Anezin, Toby Lawrence
Summary
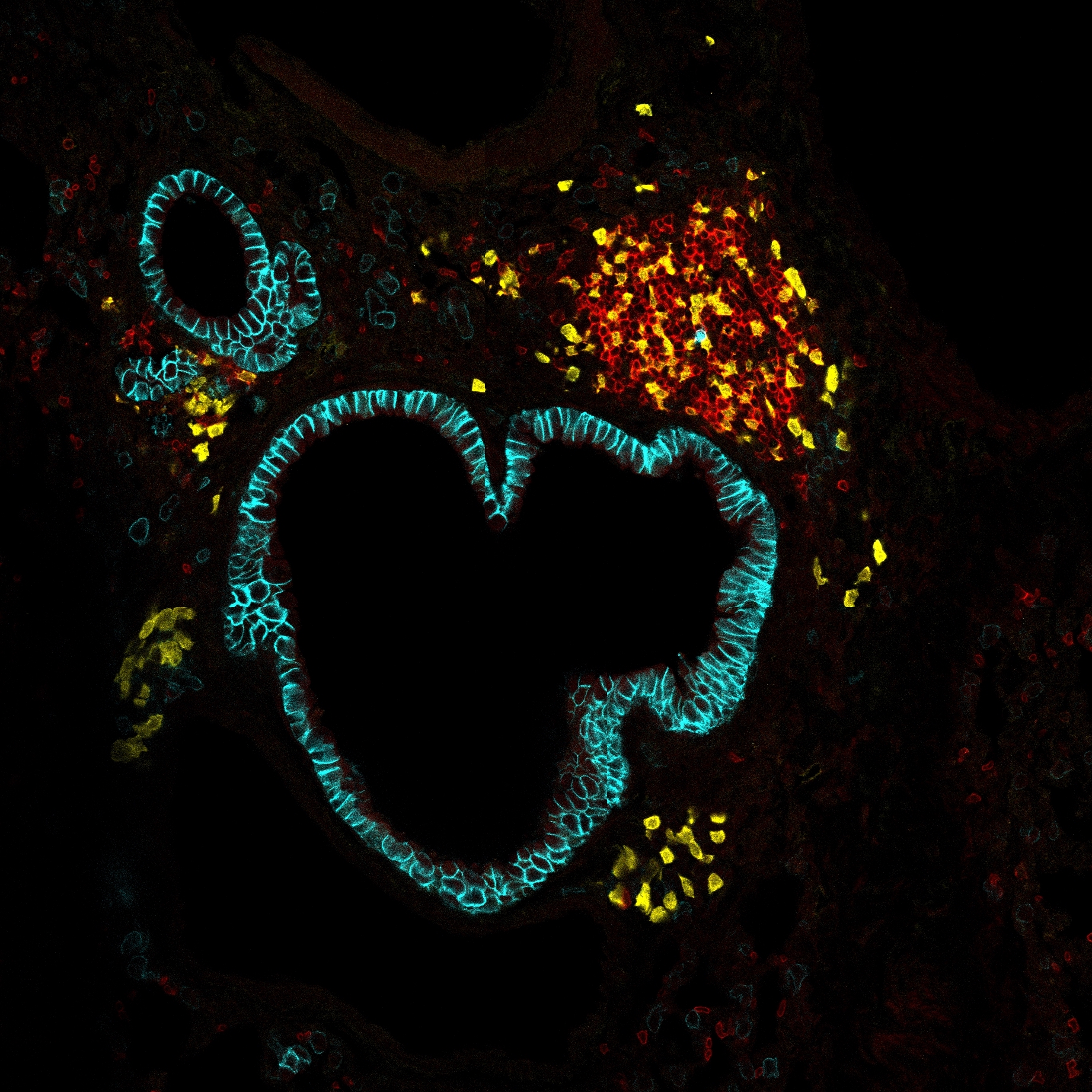
Experimental and clinical evidence suggests that tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) play important roles in cancer progression. Here, we have characterized the ontogeny and function of TAM subsets in a mouse model of metastatic ovarian cancer that is representative for visceral peritoneal metastasis. We show that the omentum is a critical premetastatic niche for development of invasive disease in this model and define a unique subset of CD163 + Tim4 + resident omental macrophages responsible for metastatic spread of ovarian cancer cells. Transcriptomic analysis showed that resident CD163 + Tim4 + omental macrophages were phenotypically distinct and maintained their resident identity during tumor growth. Selective depletion of CD163 + Tim4 + macrophages in omentum using genetic and pharmacological tools prevented tumor progression and metastatic spread of disease. These studies describe a specific role for tissue-resident macrophages in the invasive progression of metastatic ovarian cancer. The molecular pathways of cross-talk between tissue-resident macrophages and disseminated cancer cells may represent new targets to prevent metastasis and disease recurrence.
Link to HAL – hal-03082404
Link to DOI – 10.1084/jem.20191869


