Publication: Characterization of Mouse Adult Testicular Macrophage Populations by Immunofluorescence Imaging and Flow Cytometry
Published in: Bio Protoc 2019 Mar; 9(5):
Authors: Noushin Mossadegh-Keller, Michael H. Sieweke
Summary
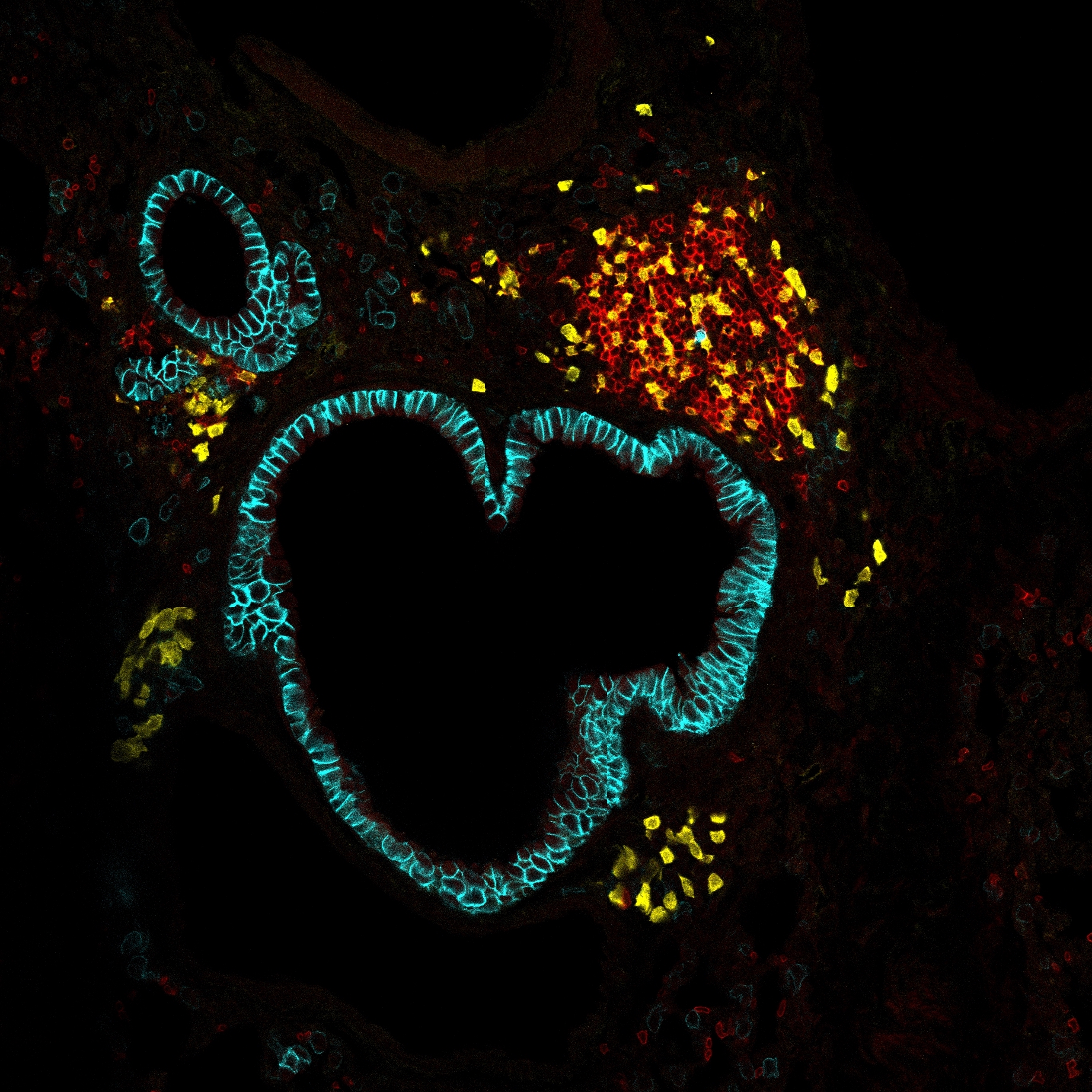
Testicular macrophages (tM phi) are the most abundant immune cells residing in the testis, an immune-privileged organ. TM phi are known to exhibit different functions, such as protecting spermatozoa from auto-immune attack by producing immunosuppressive cytokines and trophic roles in supporting spermatogenesis and male sex hormone production. They also contribute to fetal testicular development. Recently, we characterized two distinct tM phi populations based on their morphology, localization, cell surface markers, and gene expression profiling. Here, we focus and describe in detail the phenotypical distinction of these two tM phi populations by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) using multicolor panel antibodies combining with high-resolution immunofluorescence (IF) imaging. These two techniques enable to classify two tM phi populations: interstitial tM phi and peritubular tM phi.
Link to HAL – hal-02359453
Link to DOI – 10.21769/BioProtoc.3178
