À propos
Le système immunitaire se met en place pendant la vie embryonnaire et la période néonatale selon une succession d’événements finement coordonnés. Des acteurs clés de cette construction sont les cellules lymphoïdes innées (ILC), spécifiquement les Lymphoid tissue inducer cells (LTi). Ces lymphocytes interagissent avec les cellules stromales « organisatrices » pour amorcer et et organiser le dévelopement des ganglions Lymphatiques au cours de l’embryogénèse.

Au Centre d’Immunologie de Marseille–Luminy (CIML), le laboratoire de Serge van de Pavert étudie comment les ILC contribuent au développement et à la maturation du système immunitaire in vivo. Nous explorons comment les signaux dévelopementaux très précoces — environnement maternel, nutriments et signaux neuronaux — vont influencer l’éfficacité du système immunitaire tout au long de la vie. Notre approche combine génétique de la souris, perturbations fonctionnelles, microscopie avancée et analyse d’images 3D.

SPlab 5-June-2025
Axes de recherche
- Développement et fonctions des ILCs dans les tissus embryonnaires et au cours de la période néonatale et postnataux
- Contrôle cellulaire et moléculaire de l’organogenèse des ganglions lymphatiques
- Influence de l’environnement maternel (régimes alimentaire et signaux métaboliques) sur le développement du système immunitaire
- Rôle des interactions neuro–immunes dans l’organisation tissulaire
- Imagerie volumique et morphométrie computationnelle 3D
Approches & méthodes
- Génétique murine, lignage et traçage cellulaire
- Perturbations fonctionnelles in vivo (contrôle conditionnel/temporel)
- Clarification tissulaire, microscopie confocale/feuille de lumière, reconstructions volumiques
- Transcriptomique unicellulaire
- Pipelines d’analyse d’images 3D et modélisation quantitative
Équipe & Collaborations
Nous collaborons étroitement avec des partenaires en immunologie, neurobiologie et calcul pour relier les mécanismes à plusieurs échelles — des réseaux transcriptionnels jusqu’à la morphogenèse des organes.
- Lionel Spinelli, CB2M, CIML, Marseille, France
- Denis Puthier, TAGC, Marseille, France
- Andreas Diefenbach, Charité Berlin, Germany
- Alexandre Pattyn, Institut Neuroscience Montpellier, France
- Léo Guignard, IBDM, Marseille, France
- Rachel Golub, Institut Pasteur, Paris, France
- Christelle Harly, UMR_S 1307 Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie et Immunologie Intégrée Nantes Angers
- Andrea Brendolan, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan, Italie
- Fabio Santori, University of Georgia, USA
- Heather Etchevers, IMM, Marseille, France
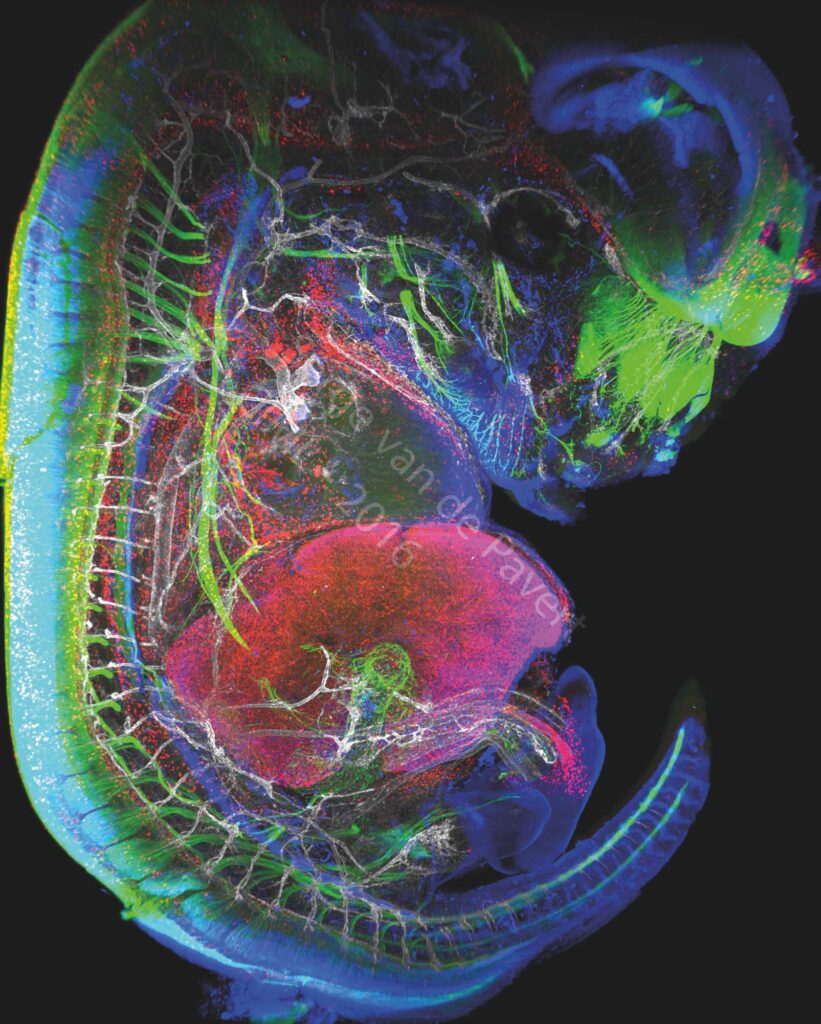
“Immunofluorescent staining of a complete mouse E13.5 embryo reveals neurons (labeled with BetaIII Tubulin), macrophages and lymphatic endothelial cells in red (labeled with Lyve-1), the nuclei of specific neurons and lymphatic endothelial cells are marked in blue (Prox1 labeling) and the vascular network in white (Pecam-1 labeling). The eye of the embryo and the nasal neurons can be seen in green. On the left, the spinal cord is marked in green. The vertebrae are visible through the marking of the dorsal root ganglia in green, and blood vessels marked in white. The heart is visible just above the liver which is labeled with LYVE-1 antibody. The embryonic intestine, not far from the liver, is visualized by the innervation of neurons in green. The umbilical cord can be observed by neighboring white blood vessels and macrophages in red. This picture was generated in the study on the formation of lymph nodes and lymphatic system. Their formation, initiated in the embryonic stage, can be modified by changing certain dietary factors affecting cell differentiation. These visualizations are therefore intended to analyze the movements of cells involved in the formation of the lymphatic system.” Image Serge van de Pavert/CIML.
Projets
Project : SensoSkin Apical extracellular matrix (aECM) shapes and protects the epithelium in all organisms. We previously showed that like […]

Projet Amidex : ELNINo Nous analysons comment les signaux neuronaux s’intègrent aux programmes immunitaires et stromaux pour orchestrer l’organogenèse des ganglions. En […]

Project : CholControl You are what your mother ate Impact transgénérationnel des régimes maternels via la régulation de l’activité RORγt […]