Publication: Reticular Fibroblasts Expressing the Transcription Factor WT1 Define a Stromal Niche that Maintains and Replenishes Splenic Red Pulp Macrophages
Publié dans: Immunity, 2020, 53 (1), pp.127 - 142.e7. ⟨10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.008⟩
Auteurs: Alicia Bellomo, Isabelle Mondor, Lionel Spinelli, Marine Lagueyrie, Benjamin J Stewart, Nicolas Brouilly, Bernard Malissen, Menna R Clatworthy, Marc Bajenoff
Résumé
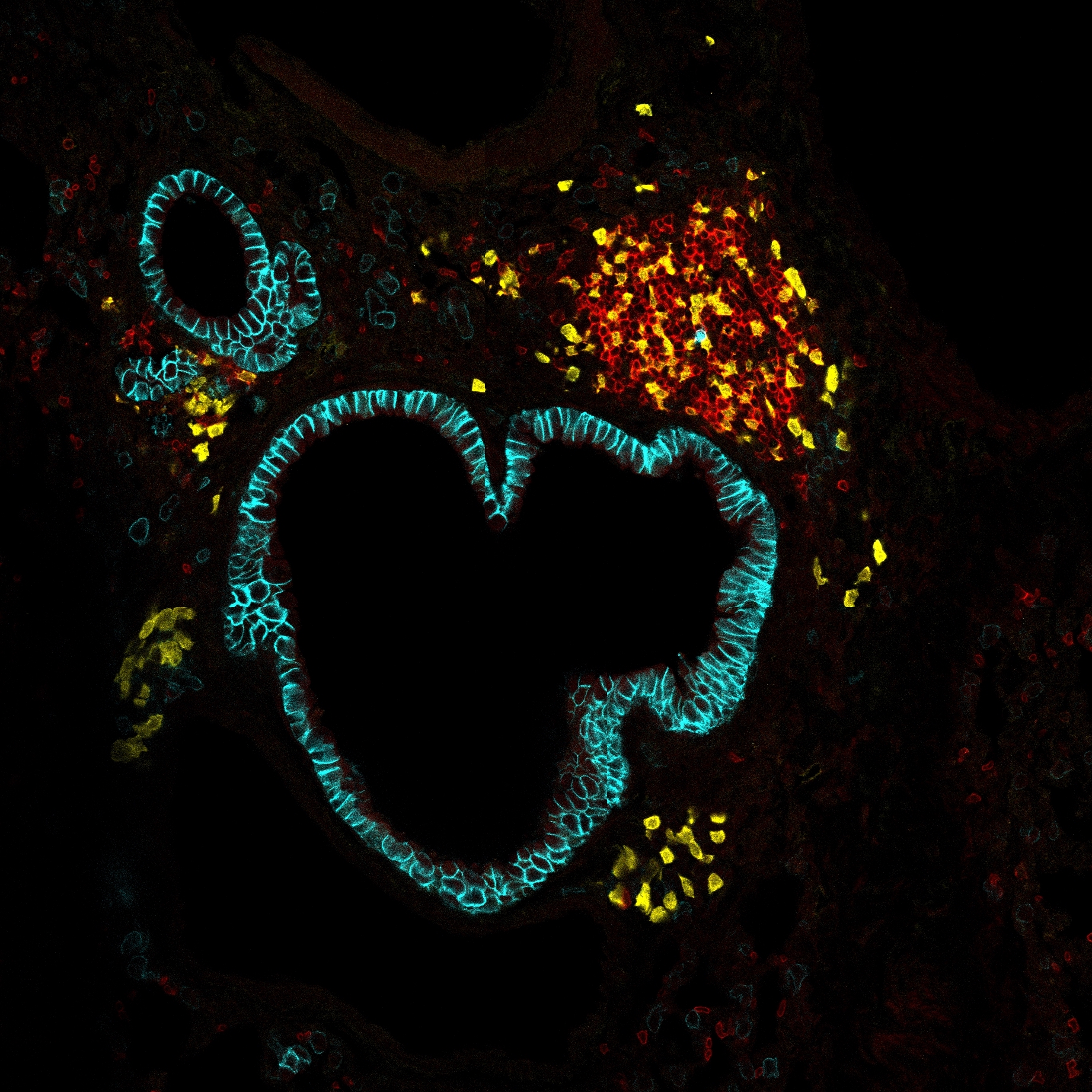
Located within red pulp cords, splenic red pulp macrophages (RPMs) are constantly exposed to the bloodflow, clearing senescent red blood cells (RBCs) and recycling iron from hemoglobin. Here, we studied themechanisms underlying RPM homeostasis, focusing on the involvement of stromal cells as these cellsperform anchoring and nurturing macrophage niche functions in lymph nodes and liver. Microscopy revealedthat RPMs are embedded in a reticular meshwork of red pulp fibroblasts characterized by the expression ofthe transcription factor Wilms’ Tumor 1 (WT1) and colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1). Conditional deletion ofCsf1in WT1+red pulp fibroblasts, but not white pulp fibroblasts, drastically altered the RPM network withoutaltering circulating CSF1 levels. Upon RPM depletion, red pulp fibroblasts transiently produced the mono-cyte chemoattractants CCL2 and CCL7, thereby contributing to the replenishment of the RPM network.Thus, red pulp fibroblasts anchor and nurture RPM, a function likely conserved in humans.
Lien vers Pubmed [PMID] – 32562599
Lien vers HAL – hal-03013466
Lien vers le DOI – 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.008