Publication: Innate lymphoid cells: major players in inflammatory diseases
Publié dans: Nature Reviews Immunology, 2017, 17 (11), pp.665-678. ⟨10.1038/nri.2017.86⟩
Auteurs: Mikael Ebbo, Adeline Crinier, Frederic Vely, Eric Vivier
Résumé
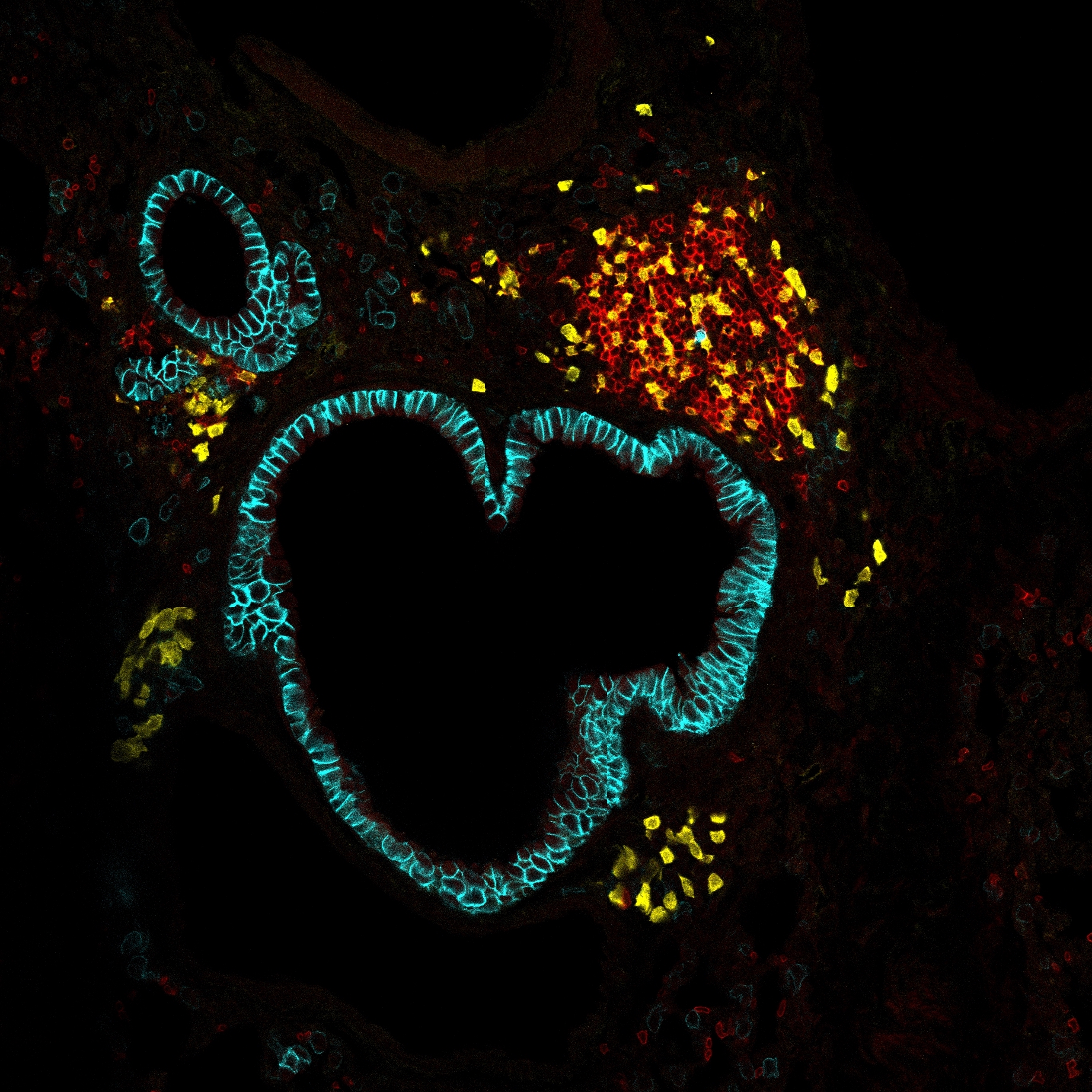
Recent years have seen a marked increase in our understanding of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs). ILCs can be classified into different groups based on their similarity to T cell subsets in terms of their expression of key transcription factors and cytokine production. Various immunological functions of ILCs have been described, and increasing numbers of studies have implicated these cells in inflammatory disorders. Here, we detail the roles of ILCs in inflammatory diseases; we cover type 2 inflammatory diseases (such as asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis and atopic dermatitis), as well as inflammatory bowel diseases, psoriasis and other systemic or organ-specific inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Future directions in the field are discussed, together with potential avenues of treatment.
Lien vers HAL – amu-01764670
Lien vers le DOI – 10.1038/nri.2017.86