Publication: T Cell Zone Resident Macrophages Silently Dispose of Apoptotic Cells in the Lymph Node.
Publié dans: Immunity 2017 Aug; 47(2): 349-362.e5
Auteurs: Baratin M, Simon L, Jorquera A, Ghigo C, Dembele D, Nowak J, Gentek R, Wienert S, Klauschen F, Malissen B, Dalod M, Bajénoff M
Résumé
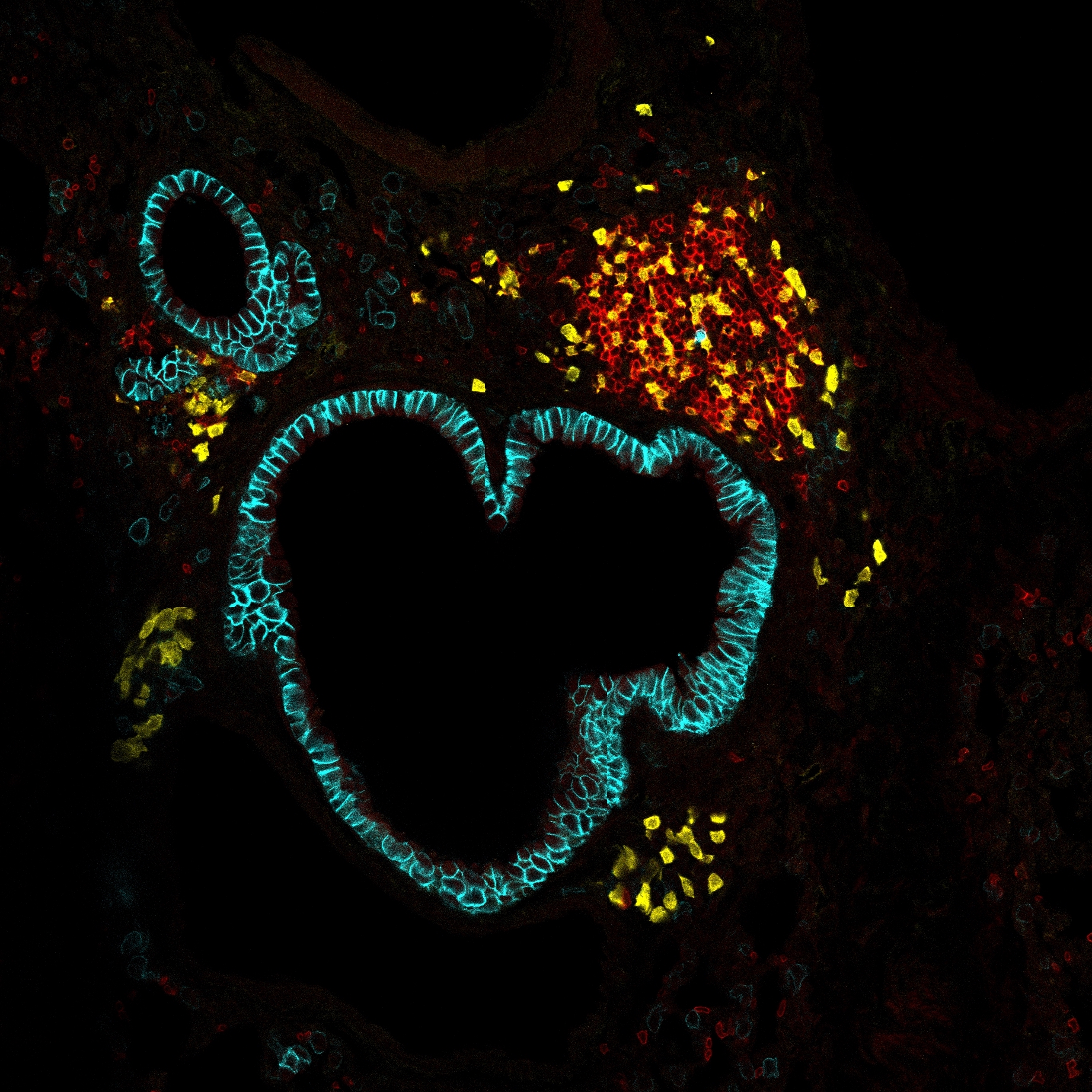
In lymph nodes (LNs), dendritic cells (DCs) are thought to dispose of apoptotic cells, a function pertaining to macrophages in other tissues. We found that a population of CX3CR1+ MERTK+ cells located in the T cell zone of LNs, previously identified as DCs, are efferocytic macrophages. Lineage-tracing experiments and shield chimeras indicated that these T zone macrophages (TZM) are long-lived macrophages seeded in utero and slowly replaced by blood monocytes after birth. Imaging the LNs of mice in which TZM and DCs express different fluorescent proteins revealed that TZM-and not DCs-act as the only professional scavengers, clearing apoptotic cells in the LN T cell zone in a CX3CR1-dependent manner. Furthermore, similar to other macrophages, TZM appear inefficient in priming CD4 T cells. Thus, efferocytosis and T cell activation in the LN are uncoupled processes designated to macrophages and DCs, respectively, with implications to the maintenance of immune homeostasis.
Lien vers Pubmed [PMID] – 28801233
Lien vers le DOI – 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.07.019