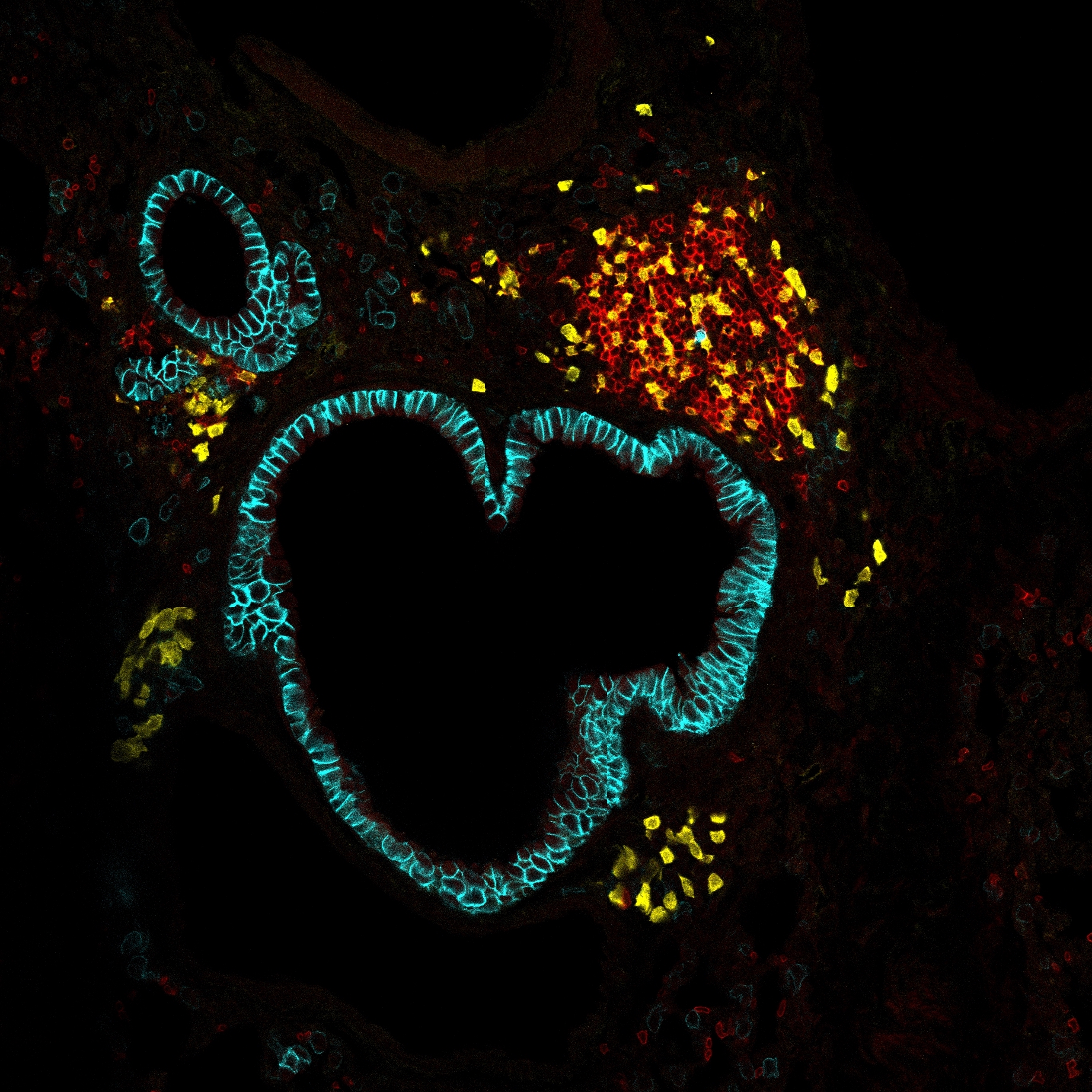

Publication: Lymphotoxin limits Foxp3+ regulatory T cell development from Foxp3lo precursors via IL-4 signaling.
Publié dans: Nat Commun 2024 Aug; 15(1): 6976
Auteurs: Borelli A, Santamaria JC, Zamit C, Apert C, Chevallier J, Pierre P, Argüello RJ, Spinelli L, Irla M
Résumé
Regulatory T cells (Treg) are critical players of immune tolerance that develop in the thymus via two distinct developmental pathways involving CD25+Foxp3- and CD25-Foxp3lo precursors. However, the mechanisms regulating the recently identified Foxp3lo precursor pathway remain unclear. Here, we find that the membrane-bound lymphotoxin α1β2 (LTα1β2) heterocomplex is upregulated during Treg development upon TCR/CD28 and IL-2 stimulation. We show that Lta expression limits the maturational development of Treg from Foxp3lo precursors by regulating their proliferation, survival, and metabolic profile. Transgenic reporter mice and transcriptomic analyses further reveal that medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTEC) constitute an unexpected source of IL-4. We demonstrate that LTα1β2-lymphotoxin β receptor-mediated interactions with mTEC limit Treg development by down-regulating IL-4 expression in mTEC. Collectively, our findings identify the lymphotoxin axis as the first inhibitory checkpoint of thymic Treg development that fine-tunes the Foxp3lo Treg precursor pathway by limiting IL-4 availability.
Lien vers Pubmed [PMID] – 39143070
Lien vers HAL – amu-04780863
Lien vers le DOI – 10.1038/s41467-024-51164-5
